Welcome, gentlemen and other semi-casual aficionados of men’s health. Today, we’re looking into a topic that’s absolutely crucial for your health and often, unfortunately, overlooked: antioxidants and their role in your diet. While you may have heard the term “antioxidants” thrown around loosely, there’s actually a lot of solid science behind their importance and it’s certainly something worth paying attention to if you care to live life as fully as you can.
What are Antioxidants?
Simply put, antioxidants are compounds that help manage oxidative stress in your body. Oxidative stress occurs when harmful molecules called free radicals outnumber the antioxidants in your system, leading to cellular damage.
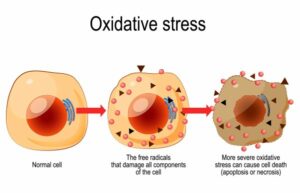
Why does this matter? Because oxidative stress is directly linked to many serious health issues, including heart disease, cancer, and aging-related conditions. Antioxidants help us to neutralize free radicals and in turn offer protection against the negative effects oxidative stress has on various bodily processes.
But here’s the catch: your body doesn’t really produce antioxidants (other than glutathione) on its own, so the only way to get them is by consuming them, typically and preferably from food. This is where the importance of an antioxidant-rich diet comes into play.
In this blog, we’ll explore why antioxidants are much more than just a passing health craze. We’ll discuss their significance for men’s health and provide practical tips for incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your daily routine. Let’s look beyond the buzzword.
Understanding Antioxidants
We gave the overview above, but let’s take a closer look at antioxidants and how they work in your body.
Antioxidants are the often unsung heroes of biology, quietly going about their business to keep you healthy. These compounds come in various forms, including vitamins like C and E, minerals like selenium, and phytochemicals found in plants.
Their main job is to neutralize free radicals, molecules that can wreak havoc on your cells. Picture antioxidants as the firefighters, rushing in to extinguish the flames of oxidative stress before they cause more damage than necessary.
The function of antioxidants is based on electrons. Free radicals are unstable molecules that are missing an electron, so they essentially steal electrons from other molecules in your body. This process can set off a chain reaction of damage. Antioxidants, on the other hand, donate electrons to stabilize free radicals, ending their destructive processes.
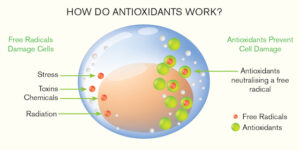
By doing so, antioxidants help protect your cells from oxidative damage and maintain your overall health. They’re a major part of your body’s defense system, standing guard against the wear and tear of daily life.
The Link Between Oxidative Stress and Men’s Health
Now that we understand the role of antioxidants a bit better, let’s look at why oxidative stress poses a significant threat to men’s health.
Oxidative stress occurs when the production of free radicals overwhelms the body’s ability to neutralize them with antioxidants. This imbalance leads to damage at the cellular level, affecting various bodily functions.
For men specifically, oxidative stress has been closely linked to several health issues, including cardiovascular issues such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. The damaging effects of oxidative stress on lipids, proteins, and DNA contribute to the development and progression of these conditions. This is a huge deal because cardiovascular diseases in general are known to be the number one killer of both men and women.

Oxidative stress also plays a role in the pathogenesis (development) of cancer, another major concern for men’s health. Free radicals can induce DNA mutations and promote the proliferation of cancerous cells, increasing the risk of various types of cancer, including prostate cancer, one of the most common cancers among men.
Beyond cardiovascular diseases and cancer, oxidative stress is implicated in age-related conditions that disproportionately affect men, such as erectile dysfunction and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The oxidative damage to blood vessels and nerves contributes to the development of erectile dysfunction, while inflammation and oxidative stress are involved in the pathogenesis of BPH.
Understanding this connection between oxidative stress and these major health issues underscores the importance of maintaining a balance between antioxidants and free radicals in the body. In the following sections, we’ll explore how an antioxidant-rich diet can help mitigate oxidative stress and promote better health outcomes for men.
Benefits of an Antioxidant-Rich Diet for Men
Now that we’ve established the significance of antioxidants, let’s look into the specific benefits of incorporating an antioxidant-rich diet into your lifestyle because, as mentioned in the introduction, we mostly get them from our diet.
1. Improved Cardiovascular Health: Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting against cardiovascular diseases by reducing oxidative damage to blood vessels and lowering inflammation. Studies have shown that diets rich in antioxidants, particularly those found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains, are associated with a lower risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. Cancer Prevention: Antioxidants have been studied for their potential in preventing cancer by neutralizing free radicals and inhibiting the growth of cancerous cells. While more research is needed to fully understand their role in cancer prevention, observational studies suggest that diets high in antioxidants may lower the risk of certain cancers, including prostate cancer, which is of particular concern for men.
3. Enhanced Fertility and Sexual Health: Oxidative stress can negatively impact male reproductive health by causing damage to sperm DNA and impairing sperm function. Antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium have been shown to improve sperm quality and motility, thereby enhancing fertility. Additionally, antioxidants may help alleviate oxidative stress-related erectile dysfunction by improving blood flow and vascular function.
4. Supporting Overall Vitality and Longevity: Beyond specific health conditions, an antioxidant-rich diet can contribute to overall well-being and longevity. By reducing oxidative damage and inflammation, antioxidants help preserve cellular function and slow down the aging process. This can translate into improved energy levels, cognitive function, and quality of life as you age.
By prioritizing antioxidant-rich foods in your diet, such as colorful fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and nutrient-dense proteins, you can build some serious benefits and safeguard your health for years to come. In the next section, we’ll explore practical strategies for incorporating these nutrient-packed foods into your daily meals and snacks, making healthy eating a sustainable and enjoyable part of your lifestyle.
Sources of Antioxidants in Men’s Diet
Let’s lay out a solid array of foods that can help boost your antioxidant intake.
1. Fruits and Vegetables: Colorful fruits and vegetables are powerhouse sources of antioxidants. Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are particularly rich in antioxidants like vitamin C and anthocyanins. Other antioxidant-packed options include leafy greens like spinach and kale, as well as brightly colored vegetables like bell peppers, tomatoes, and carrots.
2. Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are not only rich in healthy fats and protein but also provide a significant dose of antioxidants. Almonds, walnuts, and pecans are excellent choices, along with seeds like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds. Incorporating a handful of nuts or seeds into your daily snack routine can boost your antioxidant intake significantly. Opt for sprouted versions of these whenever you for extra health points.
3. Whole Grains: Whole grains are another valuable source of antioxidants, along with essential nutrients like fiber and B vitamins. Opt for whole-grain options such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley to maximize your antioxidant intake while promoting heart health and digestion.
4. Nutrient-Dense Proteins: While fruits and vegetables tend to steal the spotlight, nutrient-dense proteins also largely contribute to your antioxidant intake. Fish, poultry, and lean cuts of beef or pork contain antioxidants like selenium and zinc, as well as other essential nutrients for muscle growth and repair.
5. Herbs and Spices: Also often overlooked are antioxidant power of herbs and spices; these seasonings do so much more than simply enhance the flavor of your meals and can actually add significant nutritional value. Turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, oregano, and cloves are just a few examples of antioxidant-rich herbs and spices that can elevate your culinary game while simultaneously boosting your health.
Incorporating a variety of these antioxidant-rich foods into your diet can help ensure that you’re getting a diverse range of nutrients to support your overall health and well-being.
Lifestyle Factors That Support Antioxidant Activity
In addition to dietary choices, certain lifestyle factors play a crucial role in supporting antioxidant activity and overall health. Here are some key lifestyle habits to consider:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity not only strengthens your muscles and improves cardiovascular health but also enhances antioxidant defenses in your body. Exercise stimulates the production of our main endogenous antioxidant glutathione, while promoting blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days per week.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can increase oxidative stress levels in the body, leading to cellular damage and inflammation. Incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Prioritizing self-care activities and finding healthy outlets for stress can have a positive impact on your overall well-being and antioxidant status.

- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for cellular repair, hormone regulation, and immune function, all of which are closely linked to antioxidant activity. Aim for 7 hours minimum and 9 hours maximum of uninterrupted and quality sleep (prioritize a dark and cold room without eating for a few hours prior) each night to allow your body to recharge and optimize antioxidant reserves. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment can help improve sleep quality and support antioxidant function.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking, particularly conventional cigarettes, releases numerous harmful chemicals that increase oxidative stress and damage cellular structures. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce oxidative damage and lower the risk of developing smoking-related diseases. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can impair antioxidant defenses and contribute to oxidative stress. Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels, defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.

By incorporating these tips into your lifestyle, you can massively enhance antioxidant activity, reduce oxidative stress, and support overall health and longevity. Making informed choices about diet, exercise, stress management, and substance use can significantly empower you to take control of your health and optimize your well-being.
Closing Thoughts
As we come to the end of our exploration into the importance of an antioxidant-rich diet and lifestyle for men’s health, one thing is clear: prioritizing antioxidants isn’t just a health trend—it’s a fundamental aspect of maintaining vitality and well-being.
Throughout this journey, we’ve uncovered the vital role antioxidants play in combating oxidative stress, a common culprit behind various health issues affecting men. From cardiovascular disease to cancer to reproductive health, antioxidants serve as powerful defenders, shielding our cells from damage and promoting optimal function.
We’ve learned that achieving an antioxidant-rich diet is totally within reach, thanks to a diverse array of nutrient-packed foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and nutrient-dense proteins. By incorporating these foods into our meals and snacks, we can nourish our bodies with the essential nutrients needed to thrive.
But it’s not just about what we eat. Lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, stress management, adequate sleep, and avoiding harmful substances like smoking and excessive alcohol also play a crucial role in supporting antioxidant activity and overall health.
So, as we conclude this discussion, let’s take this knowledge and turn it into action. Let’s commit to making conscious choices that prioritize our health — whether it’s choosing antioxidant-rich foods, staying active, managing stress, or getting quality sleep.
By embracing these habits and incorporating them into our daily lives, we can empower ourselves to take control of our health, boost our antioxidant defenses, and live life to the fullest. Here’s to a future filled with vitality, longevity, and well-being. Cheers to your health!









