Testosterone. The word alone evokes images of peak masculinity—strength, confidence, resilience, and the ability to grow a proper beard. But there’s a problem. Over the last few decades, men’s testosterone levels have been plummeting at an alarming rate. We’re not talking about the natural decline that happens with aging—we’re talking about a downward spiral that spans all age groups, including young men in their supposed prime. It’s not just the couch potatoes either; even active, seemingly healthy men are seeing lower levels than their fathers and grandfathers did. The consequences? Everything from decreased libido and muscle loss to depression, brain fog, and increased mortality risk.
So, what gives? Many blame plastics, pesticides, obesity, or even a cultural shift that discourages traditional masculinity. But while these factors might play a role, the real culprit could be lurking within your cells—specifically, your mitochondria. These tiny powerhouses of the cell are responsible for producing energy, and as it turns out, they’re also directly involved in testosterone production. If your mitochondria are dysfunctional, your testosterone levels will take a nosedive. But here’s the good news: by improving mitochondrial health, you can reverse this trend and reclaim your vitality. In this deep dive, we’ll break down the connection between mitochondria and testosterone and explore the most effective ways to optimize both.
The Great Testosterone Decline: What’s Really Happening?
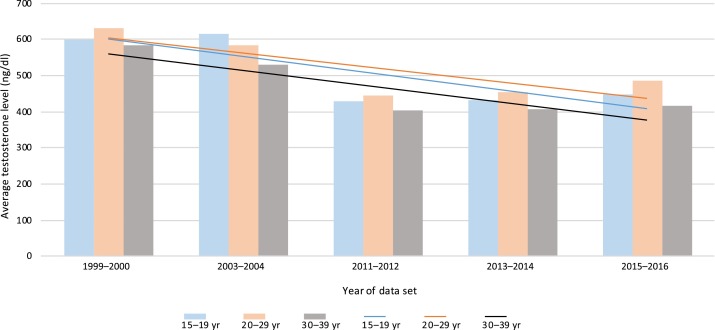
Testosterone levels in men have been on a downward spiral for decades. It’s not just aging—though that’s the easy scapegoat. Even young men, supposedly at their hormonal peak, are walking around with testosterone levels that would make their grandfathers shake their heads in disappointment. Research has shown that total testosterone declined by a staggering one-third from 1999 to 2011 across all age groups, and it doesn’t seem to be slowing down.
Many blame modern lifestyle factors—endocrine-disrupting chemicals, sedentary habits, poor nutrition, and even social shifts that discourage traditional masculinity. While all of these play major roles, there’s one root cause that often gets overlooked: mitochondrial dysfunction. Since testosterone synthesis begins in the mitochondria, compromised mitochondrial function means compromised testosterone production. If your mitochondria aren’t working efficiently, your testosterone levels will take a hit. And if that doesn’t sound like a problem, consider that low testosterone is associated with depression, sexual dysfunction, brain fog, muscle loss, and even increased mortality.
Mitochondria: The Tiny Power Plants Behind Your Manhood
Most people know mitochondria as the “powerhouses of the cell.” That’s a solid high school biology definition, but it barely scratches the surface. Mitochondria are responsible for energy production, metabolism, cellular repair, and yes—hormone synthesis. Testosterone is made from cholesterol, but it doesn’t just appear out of thin air. The transformation of cholesterol into pregnenolone—the precursor to all steroid hormones—occurs in the mitochondria. The enzyme responsible for this conversion, P450scc, is found within the inner mitochondrial membrane. In other words, if your mitochondria aren’t firing on all cylinders, your testosterone levels will plummet.
The real kicker? Mitochondrial dysfunction is more common than ever, thanks to poor diet, chronic stress, environmental toxins, and a lack of hormetic stressors (the good kind of stress that makes your body adapt and grow stronger). If you’re insulin-resistant, inflamed, or living off processed foods, your mitochondria are likely in trouble—and so is your testosterone.
Insulin Resistance: The Silent Testosterone Killer
One of the clearest indicators of mitochondrial dysfunction is insulin resistance—a state where your cells stop responding to insulin, leading to chronically high blood sugar and inflammation. It’s also strongly associated with low testosterone levels.
Here’s why: Mitochondria process glucose for energy—but when they’re damaged, they can’t keep up with demand, leading to metabolic dysfunction. Insulin resistance leads to increased fat storage, especially visceral fat, which converts testosterone into estrogen via the aromatase enzyme. High triglyceride-to-HDL ratios (a marker of insulin resistance) correlate with low testosterone. If you want to fix your testosterone, you need to fix your mitochondrial health—and that starts with improving insulin sensitivity.
How to Supercharge Your Mitochondria (and Your Testosterone)
1. Cold Therapy: Ice Your Way to Higher T Levels
Ice baths aren’t just for post-workout recovery. Cold exposure triggers mitophagy (removal of damaged mitochondria) and mitobiogenesis (creation of new mitochondria), effectively “cleaning house” and making your cells more efficient. In one study, men who incorporated ice baths into their routine saw a boost in testosterone levels, along with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation. Personal experiences continue to reinforce this truth, one standout being Morozko Forge CEO Thomas P. Seager, PhD. When Seager first experimented with ice baths, he discovered that eight months of consistent cold exposure skyrocketed his total testosterone from 700 to an impressive 1180 ng/dL—a transformation that speaks volumes about the power of mitochondrial optimization.
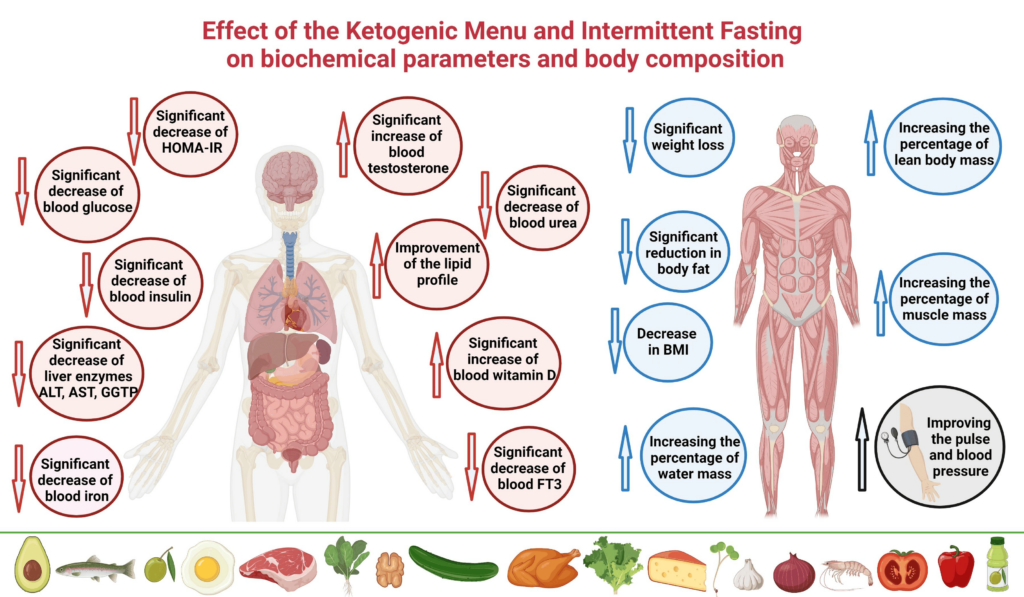
2. Intermittent Fasting & Ketosis: Give Your Mitochondria a Break
When you eat all day, your mitochondria are constantly working. Giving them a break with intermittent fasting or ketosis can improve mitochondrial efficiency and testosterone production. Research shows that low-carb diets and fasting nearly doubled testosterone levels in a 23-year-old subject over 13 weeks. Fasting also increases autophagy, a process that removes dysfunctional mitochondria and replaces them with healthier ones. If you’re insulin-resistant or struggling with low testosterone, fasting is one of the best metabolic resets you can do.
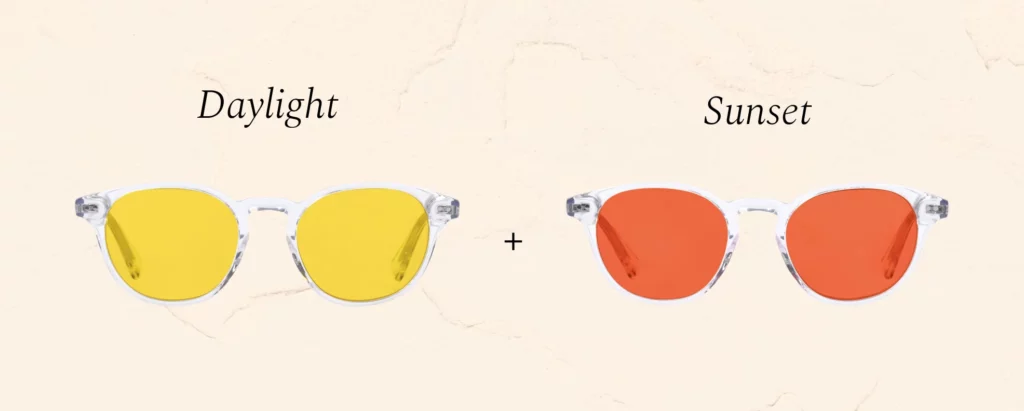
3. Fix Your Light Exposure: Melatonin, Red Light Therapy, and Mitochondria
Your mitochondria rely on melatonin as a protective antioxidant. However, blue light exposure at night disrupts melatonin production, leaving your mitochondria vulnerable to oxidative damage. Fixing this is simple: Get morning sunlight to regulate your circadian rhythm. Avoid blue light at night (use blue-light blocking glasses). Sleep in a pitch-black room to maximize melatonin production. Use red light therapy, which has been shown to support mitochondrial function and enhance testosterone production by stimulating ATP production in cells.
4. EMF Protection: Guard Your Mitochondria with Aires Tech
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) from Wi-Fi, cell phones, and other electronic devices have been linked to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Chronic exposure to EMFs can impair mitochondrial efficiency and contribute to hormonal imbalances, including lower testosterone. Aires Tech offers advanced EMF protection technology that neutralizes negative effects, supporting overall cellular health and optimizing testosterone levels.
5. Ditch Seed Oils: Stop Poisoning Your Cell Membranes
Your mitochondrial membranes are made of fat—and the type of fat you eat determines how well they function. Traditional diets had a 1:1 ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fats, but thanks to processed foods loaded with seed oils (soybean, canola, corn), that ratio is now 20:1 or worse. This excess of omega-6 fats leads to dysfunctional mitochondrial membranes, impairing testosterone production. To fix this: Avoid seed oils (read labels—they’re everywhere). Prioritize saturated fats (grass-fed beef, eggs, butter, tallow). Get more omega-3s (wild-caught salmon, sardines, pastured eggs).
6. Strength Training: The Mitochondrial and Testosterone Boosting Workout
Strength training is one of the best natural ways to boost testosterone and mitochondrial function. Lifting weights increases mitochondrial biogenesis, while compound movements like squats and deadlifts trigger testosterone production. For best results: Lift heavy (4-6 rep range for compound lifts). Train legs—squats and deadlifts cause a larger testosterone spike. Prioritize recovery (mitochondria repair when you rest).
The Bottom Line: Fix Your Mitochondria, Fix Your Testosterone
If your testosterone levels are plummeting, your mitochondria are likely at the root of the problem. While environmental toxins, stress, and modern diet play a role, mitochondrial dysfunction is the silent killer of men’s hormones. The good news? You can reverse the damage. Cold therapy, fasting, proper light exposure, avoiding seed oils, and lifting heavy are all proven strategies to revitalize your mitochondria and get your testosterone levels back where they should be. In a world where declining testosterone is seen as inevitable, be the exception. Take care of your mitochondria, and they’ll take care of you.